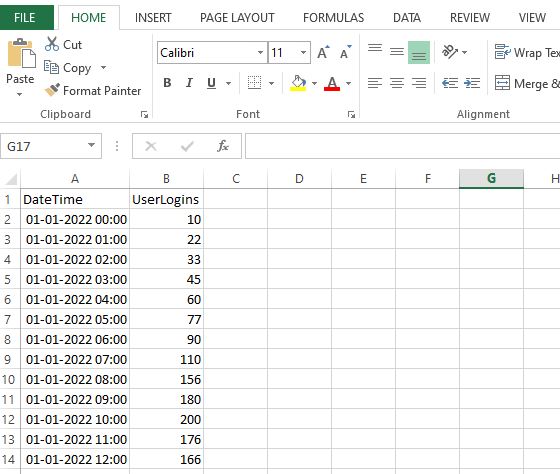
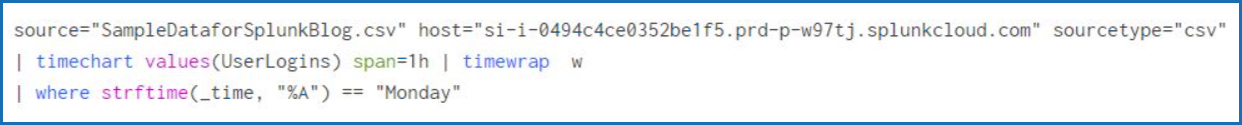
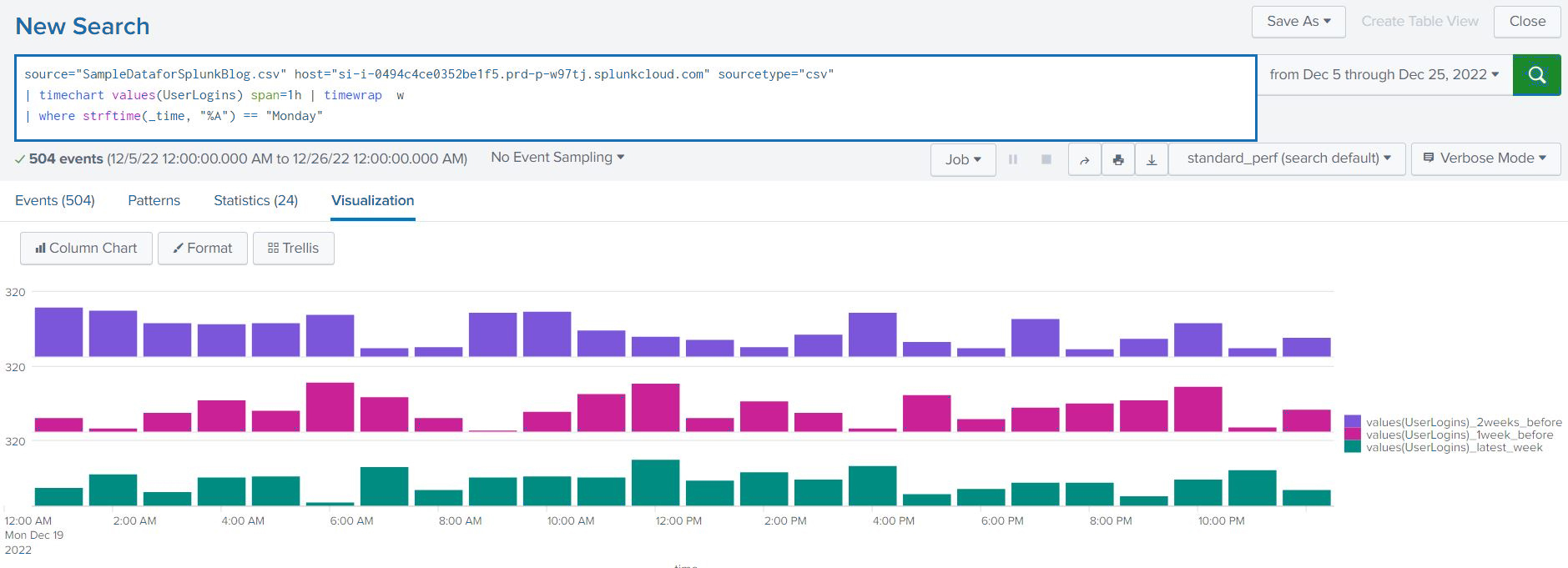
Artificial Intelligence is currently one of the most talked-about subjects, garnering more attention than ever before in its history since the term was initially coined in 1940. Before delving into the intersection of AI and DevOps, let’s have a quick recap of a few key terms to establish the context.
Highlights:
|
Key Terms Related to AI & DevOps
Artificial intelligence (AI)
Artificial intelligence (AI) is a set of technologies that enable computers to perform a variety of advanced functions, including the ability to see, understand, and translate spoken and written language, analyze data, make recommendations, and more.
What is Generative AI?
Generative artificial intelligence or generative AI (also GenAI) is a type of artificial intelligence (AI) system capable of generating text, images, or other media in response to prompts.
What is DevOps?
DevOps is a methodology in the software development and IT industry. Used as a set of practices and tools, DevOps integrates and automates the work of software development (Dev) and IT operations (Ops) as a means of improving and shortening the system’s development life cycle. DevOps is complementary to agile software development; several DevOps aspects came from the agile way of working.
Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations (AIOps)
Artificial Intelligence for IT Operations (AIOps) is a term coined by Gartner in 2016 as an industry category for machine learning analytics technology that enhances IT operations analytics. AIOps is the acronym for “Artificial Intelligence Operations.” Such operational tasks include automation, performance monitoring, and event correlations, among others.
Changing Paradigm
The term “Artificial Intelligence” was first coined by the father of AI, John McCarthy, in 1956. However, the revolution of AI actually began a few years earlier, in the 1940s. (Read more)
Modern AI is capable to See (using computer vision technologies), Hear (thanks to significant advancements in speech recognition technologies), Comprehend (effectively with the help of sophisticated algorithms), Sense (more accurately due to the democratization of big data and trained machine learning models), and finally, Act (faster and more precisely than ever before in history, fueled by rapid innovations in personal computing, internet, and cloud-native technologies).
Calling it “the third run-time,” Microsoft CEO Satya Nadella said that Artificial Intelligence is the “ultimate breakthrough” technology. He stated, “The operating system was the first run-time. The second run-time you could say was the browser. The third run-time can actually be the agent because, in some sense, the agent knows you, your work context and knows the work; and that’s how we’re building Cortana, and we are giving it a really natural language understanding.”
In simple terms, AI is the ability of machines to use algorithms to learn from data, utilize the knowledge gained to make decisions similar to humans, and take actions based on achieved intelligence or defined instructions.
How is Artificial Intelligence changing DevOps?
Today, almost every aspect of our lives is directly or indirectly impacted by AI. From small businesses, startups, mid-sized companies to large enterprises and governments, AI is being actively discussed. However, with the increased attention on AI, there is also some amount of hype leading to certain negative perceptions about its impact on the human workforce and jobs. In recent years, the classic debates about computers and machines taking over human jobs have shifted towards discussions about AI and robots taking over jobs.
DevOps, like every other aspect of business and personal lives, is also undergoing a transformation as AI takes a more central role in conversations. It is important to understand that with generative artificial intelligence, some of the key tasks and activities performed in DevOps can undergo changes.
1. Infrastructure Provisioning and Management
- Estimating infrastructure capacity, sizing, and autoscaling can be improved as AI can perform better and faster analysis of historical usage data to take appropriate actions.
- The integration of chatbots is a viable possibility to enhance management by providing smart prompts through desktop, browser, and mobile apps. For example, users can ask questions like “What percentage of CPU utilization?” or “How many active nodes are there in the load balancer?”, etc.
2. Security and Compliance
- Better anomaly detection and compliance reporting for endpoints can be achieved with AI. It enables quick detection of anomalous activities, reclassification of endpoints, and faster enforcement of compliance remediation compared to human intervention.
- AI-enabled agents can continuously monitor large amounts of network traffic data, proactively detect potential malware attacks, and be programmed to stop the attack or significantly reduce the attack surface.
3. Moving from Monitoring to Observability
- Predicting application performance degradation and avoiding potential downtime often requires significant human effort in monitoring and analyzing logs proactively and reactively. However, AI can be utilized to predict potential downtime more accurately. With self-healing automation, AI can proactively implement remediation steps to mitigate issues.
- By using more intelligent alerts, AI can effectively predict performance degradation, reducing alert fatigue on monitoring teams. It can also provide feedback to developers to improve logs and system performance.
- As logging and alerts become more precise, AI-driven systems can assist with initial triages, allowing teams to focus on running more reliable and stable applications for the business.
4. Automated Testing and Quality Assurance
- Hyper-automation optimizes business processes by integrating various automation tools and technologies. It goes beyond traditional test automation, incorporating AI and ML capabilities for intelligent automation of complex testing scenarios.
- This integration offers benefits such as intelligent test case generation, adaptive test execution, improved test coverage, and predictive analysis for early defect detection.
- AI and ML algorithms provide valuable insights from testing data, enabling organizations to optimize test strategies and make informed decisions.
5. Knowledge Sharing, Documentation, and Collaboration
- Generative AI systems, capable of generating text, images, or other media in response to prompts, can effectively capture knowledge and facilitate documentation. For example, consider the article -‘Move resources to a new subscription or resource group – Azure Resource Manager | Microsoft Learn,’ which was partially created with the help of artificial intelligence.

- By leveraging chatbots and virtual assistants, knowledge transfer can become more engaging and result-oriented, particularly in situations where time is a critical constraint for smooth handover between engineers.
- AI’s real-time data delivery and analysis capabilities can augment the automation of repetitive and mundane tasks, improving collaboration across cross-functional teams.
- Furthermore, AI advancements will influence existing enterprise search tools and technologies, which predominantly rely on text input and indexing models.

Challenges for Artificial Intelligence in DevOps
Considering the buzz around AI, everyone wants to quickly implement it into their systems and business processes. However, as with any new technology, there will be some uncertainty regarding its optimal utilization during the initial attempts. This uncertainty often leads to an exploratory approach, requiring multiple attempts to get it working right.
Based on our DevOps experience with numerous clients over the years, we have identified the following as the generic challenges in implementing AI in DevOps effectively.
1. Quantity and Quality of Enterprise Data
Meticulous planning is required to ensure sufficient and high-quality data availability to feed into machine learning models before further utilization.
2. Hiring and Training Skilled Workforce
Challenges in recruiting and training a skilled workforce to handle AI projects can impact the integration of AI into existing DevOps tools and systems.
3. Managing AI Models
Sustaining and managing AI models in the long run, ensuring they run without biases, misinformation, and copyright violations, necessitates specialized skills and a dedicated workforce.
4. Ethical Considerations
Addressing ethical considerations and ensuring responsible AI implementation goes beyond technical aspects, requiring close collaboration among stakeholders to ensure a responsible and ethical approach.
Final Thoughts
Over the next 10 years, AI will maintain its dominant presence in all fields of work and serve as a significant driving force behind every business idea, directly or indirectly. DevOps has already embarked on a transformational journey and will continue to witness rapid changes in the way IT and Software Services companies of all sizes embrace and innovate with it, ultimately adding value to their core business and customers.